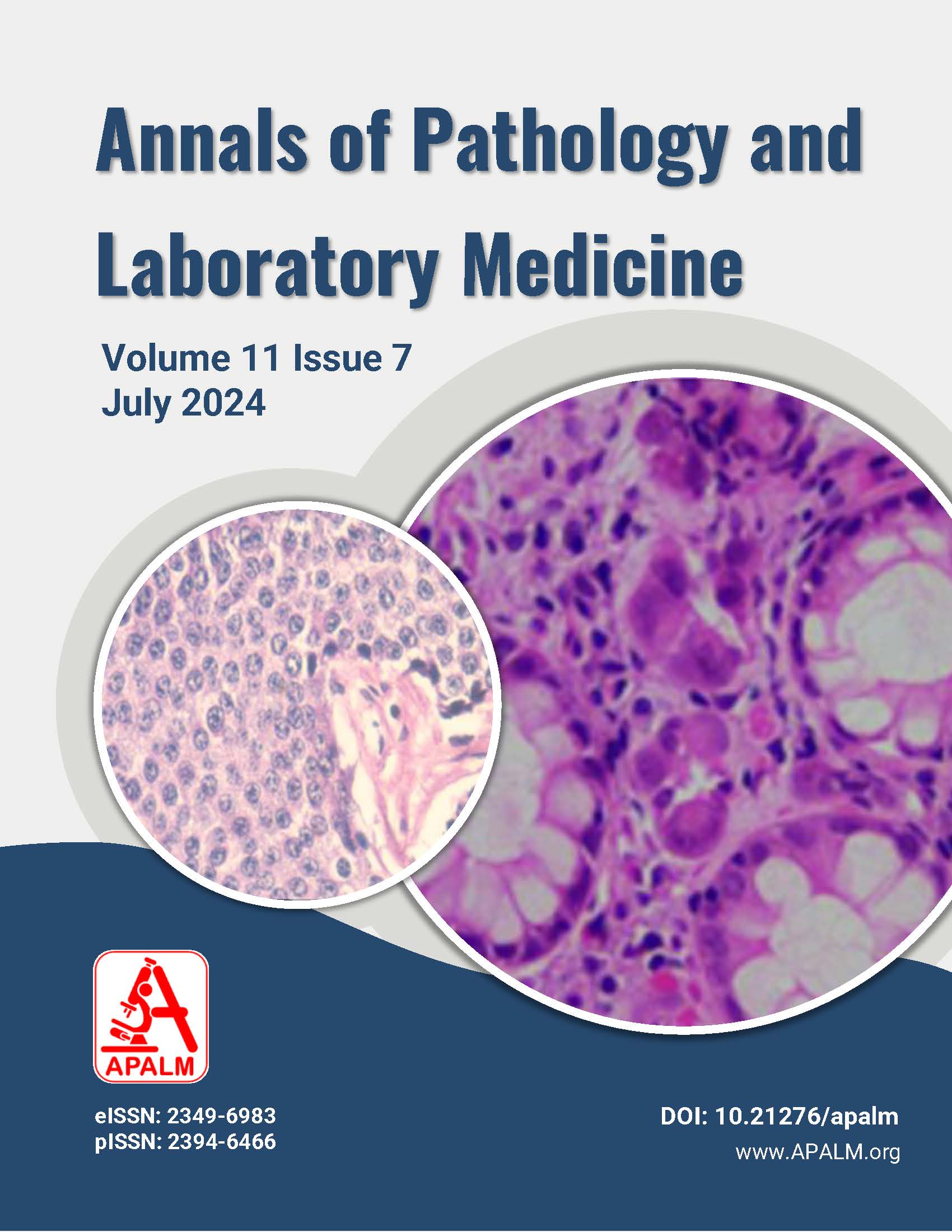
A Study of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Head and Neck Lymph Nodes
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21276/apalm.3352Keywords:
FNAC, Head and neck lymph nodes, Metastasis, Squamous cell carcinomaAbstract
Background: Lesions of the head and neck region are routinely encountered by clinicians, and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the head and neck is the sixth most common cancer worldwide. FNAC (fine-needle aspiration cytology) is one of the most important diagnostic modalities used universally in the initial assessment of patients presenting with palpable head and neck region masses. In this study, cases of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma metastasizing to lymph nodes are studied to evaluate the role of FNAC as a sole diagnostic method.
Materials and Methods: This study was conducted on 100 patients who visited the Cytopathology Department, B.J. Medical College, Civil Hospital, Ahmedabad, during the period from January 2023 to February 2024. FNAC diagnoses were correlated with detailed clinical findings and other relevant investigations.
Results: Out of 100 cases, the maximum cases were found in the age group of 51-60 years. Most of the cases were found in the right submandibular region (28%), and a total of 82% of patients had one or more histories of addiction. Cytomorphological analysis revealed that 54% of cases were SCC, 21% of cases were necrotizing SCC, 4% of cases were keratinizing SCC, 4% of cases were non-keratinizing SCC, 3% of cases were SCC with giant cell reaction, and 14% of cases were suspicious of SCC.
Conclusion: FNAC is a first-line investigation used for head and neck lymphadenopathy, including deposits of metastatic squamous cell carcinoma. Sometimes there is a diagnostic dilemma due to overlapping features on cytology, which should be kept in mind. Public awareness programs are necessary to obviate known etiological factors like tobacco.
References
Jadhav DS, Barge AK, Valand AG. Study of fine needle aspiration cytology of palpable head and neck lesions in tertiary care centre. Ind J Pathol Oncol. 2018;5(3):375-381.
Patil AA, Deshpande KAA. Neoplastic lymphadenopathy in head neck region - cytological study. Int J Health Sci Res. 2017;7(3):91-95.
Calabrese L, Jereczek-Fossa BA. Diagnosis and management of neck metastases from an unknown primary.
Johnson DE. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020 Nov 26;6(1):92.
Chute DJ. Cytology of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Variants. Diagn Cytopathol. 2010;38:65-80.
Arundhati, Jha PC. Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in Metastatic Lymph Nodes: A Study from Bihar. Ann Int Med Den Res. 2017;3(4)
.Rathod GB, Parmar P. Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Swellings of Head and Neck Region. Indian J Med Sci. 2012;66(3):49-54.
Bhavani C, Neeraja M, Varalakshmi KPV, Ramana Babu PV, Chaitanya B, Sravani P. Role of FNAC in the Diagnosis of Cervical Lymphadenopathy. Int J Med Res Rev. 2014;2(6):599-603. doi:10.17511/ijmrr.2014.i06.015.
Ding S, Guo W, Yin G, Li N, Liu H, Huang J, et al. Clinical study of poorly differentiated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a prospective cohort study in China. Ann Transl Med. 2022;10(12):703.
Kanwal M. Addiction of tobacco chewing and smoking in the patients of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A descriptive epidemiological study.
Wilkinson AR, Mahore SD, Maimoon S. FNAC in the diagnosis of lymph node malignancies: A simple and sensitive tool. Indian J Med Pediatr Oncol. 2012;33(1):21-24.
Chauhan R, Trivedi V, Rani R, Singh U. A Study of Head and Neck Cancer Patients with Reference to Tobacco Use, Gender, and Subsite Distribution.
Orell SR, Sterrett GF. Orell & Sterrett’s Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology. 5th ed.
Faquin WC, Rossi ED. The Milan System for Reporting Salivary Gland Cytopathology.
Tao L, Lefevre M. Reappraisal of metastatic lymph node topography in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.
Baruah AK, Bhuya G. Utility of the Sydney system for reporting of lymph node cytology in a tertiary health care set up of north-eastern India.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Twinkle Bhashyantkumar Thakkar, Hemina Himanshu Desai, Aesha Amrish Parikh, Bhumi Rameshchandra Bhuva, Hansa Goswami

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access at http://opcit.eprints.org/oacitation-biblio.html).